
论文题目:Engineering a Local Hydrophilic Environment in Fuel Oil for Efficient Oxidative Desulfurization with Minimum H2O2 Oxidant
论文作者:Lei Chen, Jin-Tao Ren, Hao-Yu Wang, Ming-Lei Sun, and Zhong-Yong Yuan*
发表期刊:ACS Catal.2023, 13, 18, 12125–12133
Abstract
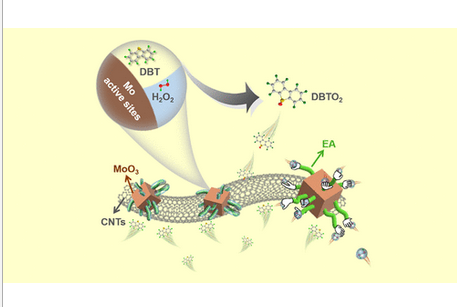
Oxidative desulfurization (ODS) using H2O2 oxidant has emerged as a viable carbon-neutral way to produce premium-grade sulfur-free fuels, yet it currently suffers from overconsumption of oxidants and low efficiency for the immiscibility and high interfacial tension of water and oil. Here, we report efficient ODS using minimal H2O2 oxidant without phase transfer agents. This is achieved by introducing organic modifiers (for example, etidronic acid (EA)) on molybdenum oxides anchored carbon nanotubes to dynamically activate Mo active sites and capture H2O2 molecules. Such in situ generated local hydrophilicity depends on the electron-donating and hydrophilic −OH functional groups in EA, which can not only endow Mo active sites with high electron density for chemisorption of H2O2 but also ensure the sufficient supply of H2O2. Combined with the substrate enrichment effect of hydrophobic porous carbon to sulfur contaminants, the efficient ODS reaction occurs at the solid–water–oil three-phase interface. The complete desulfurization was achieved within 10 min at 40 °C with an O/S ratio of 1, surpassing the optimum in the literature. This work unveils an avenue to improve ODS activity by harnessing the local reaction environment.
